IVF
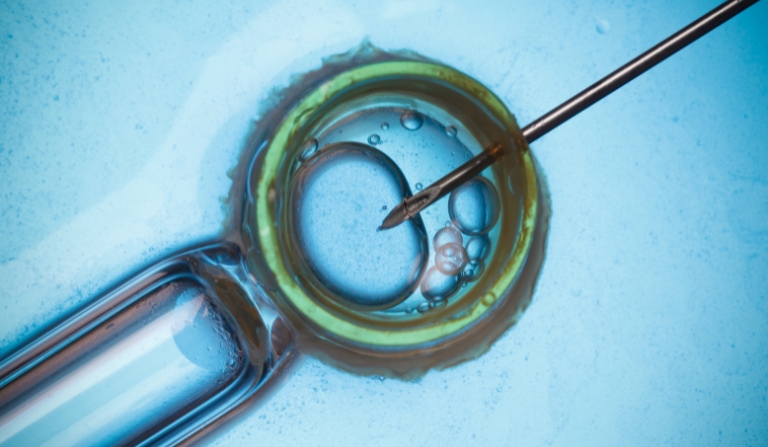
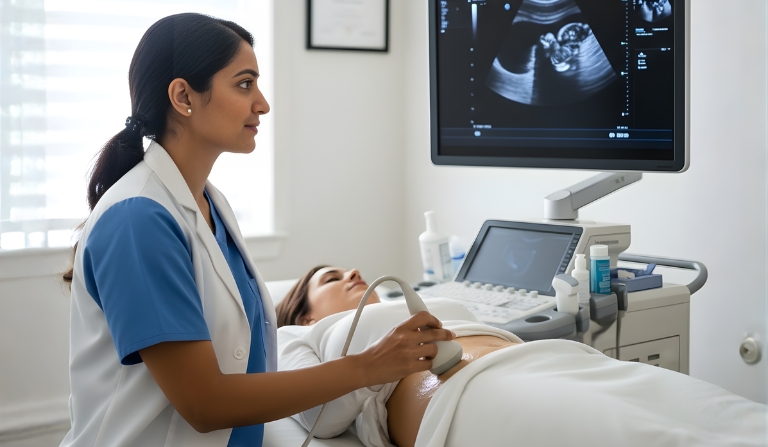
During IVF (in vitro fertilization), mature eggs are retrieved from the ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory setting. Subsequently, embryos – fertilized eggs – are carefully transferred into the uterus. A complete IVF cycle typically spans 2 to 3 weeks. This method represents the most successful form of fertility treatment involving the manipulation of eggs, embryos, and sperm, collectively known as assisted reproductive technology (ART).